To map your path from idea to revenue: validate the idea, the market, the offer, build the product, and build a repeatable sales process.
Mapping the Path from Idea to Revenue
Here are five key steps for mapping the path from an idea to early customers and early revenue. This idea to revenue approach is designed to evaluate ideas critically, identifying those that cannot sustain as independent products and thus should not receive resources. It also highlights which ideas have potential and can be developed into sellable products. This approach helps clients efficiently determine the viability of their product ideas.
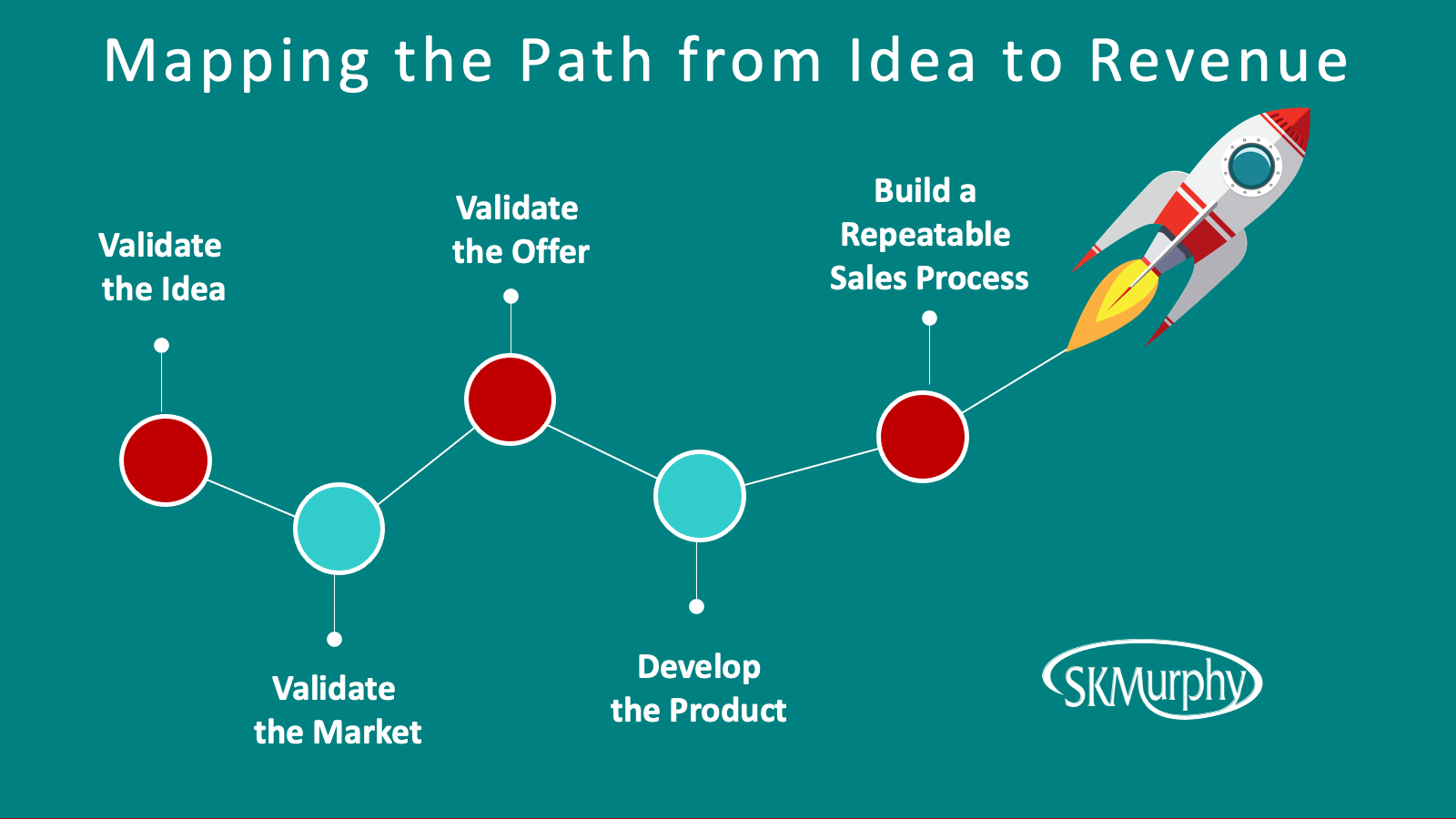
Validate the Idea
Validating the idea involves speaking to potential customers about their problems. The objective is to find someone who acknowledges the problem and is actively seeking a solution. You can refine your idea into a potential solution by talking with customers. If customers show interest, further discussion should focus on the solution’s value, asking how much they would be willing to pay to gauge the market potential. Then, you are ready to go to step two.
Validate the Market
Validate the market by confirming that there is a significant demand for your product in a niche market. This step requires researching and engaging with a broader audience to gather data on potential customers’ needs and behaviors. Key activities include: conducting interviews, figuring out who else sells to them, understanding where they hang out and who influences them, analyzing market trends, and studying competitors. The goal is to ensure that the product has a viable market size and genuine interest. Market validation helps you understand the target audience, refine the product’s value proposition, and identify the most effective marketing and sales strategies to reach potential customers.
Validate the Offer
Validate your offer by testing the appeal and feasibility of your product’s proposed value proposition, pricing, and features with potential customers. This step includes presenting the product concept to a sample audience, gathering feedback on its attractiveness, and determining whether customers are willing to pay for it. The aim is to refine the product and ensure it meets customer expectations and market demands.
At the end of this phase, you have created your business model and identified how your startup will make money. You have outlined your pricing strategy, sales channels, cost structure, and value delivery methods.
Develop the Product
In the earlier stages, you have only built enough to get feedback: presentations, datasheets, mockups, and example output or results. Now, you need to build something that will deliver value to your customers. This may involve further prototyping of early products that stay in your hands but provide outputs or results customers are willing to pay for. We have seen successful teams cobble together MVPs from off-the-shelf components for their early products or add one or two critical capabilities to an existing platform. Conduct beta testing with a select user group to gather feedback and make improvements.
Build a Repeatable Sales Process
To build a scalable sales machine: start with a clearly defined sales process you ask everyone to follow, but allow for controlled experimentation. Develop a lead generation strategy using diverse channels like inbound marketing, outbound prospecting, and partnerships. Regularly analyze data to optimize performance and identify areas for improvement. Automate repetitive tasks to increase efficiency and scale efforts. Foster continuous learning and experimentation to respond to market changes and drive sustained growth.
Idea to Revenue
We advise startups to follow a five-step approach to map their path from idea to revenue: validating the idea, validating the market, validating the offer, building the product, and building a repeatable sales process. The process begins with validating the idea by discussing potential problems with customers to refine the solution and gauge interest. Next, market validation confirms significant demand through research and engagement. Offer validation tests the value proposition and pricing with a sample audience. Product development involves building the product using agile methods and beta testing. Finally, building a repeatable sales process focuses on creating a standardized sales process, lead generation, and continuous improvement.
Resources
- 3 Equations & 3 Unknowns: Customers, Features, Message
- Startup Stages
- Market Exploration Workshop
- Landing Your First Ten Customers: Videos, Slides, and Other Resources
- Q: How Does a First Time Founder Learn Sales?
